Demystifying Enterprise Architecture with TOGAF - Understanding the Architecture Development Methodology (ADM)
In the previous article, we glanced through Enterprise Architecture as a whole and also discussed the need for an Enterprise Architecture Framework, like TOGAF.
With this article we shall continue exploring TOGAF further, and discusses TOGAF's Architecture Development Methodology (ADM).
The Architecture Development Methodology (ADM)
The Architecture Development Methodology (ADM) provides a proven and repeatable process for developing architectures.
The Scope
The scope of ADM includes or encompasses the below listed activities, which are generally carried out in iterative cycles of continuous architecture definition and realization; thus aiding a controlled transformation of an enterprises in response to business goals and opportunities -
- Establishing an architecture framework
- Developing architecture content
- Transitioning
- Governing the realization of architectures
Implementation Phases
The implementation of ADM could be envisioned across the following phases -
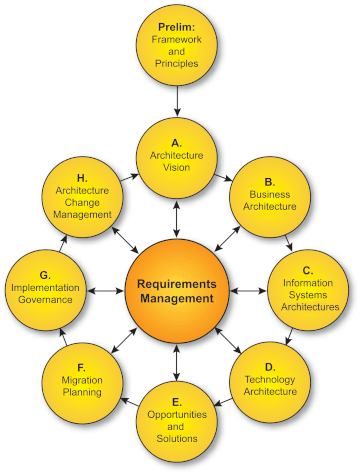
Preliminary Initiation
The Preliminary Initiation phase describes the preparation and initiation activities, required for meeting the business directive for a new enterprise architecture, including the definition of an Organization-Specific Architecture framework and the definition of core principles.
Architecture Vision Setup
The Architecture Vision Setup phase describes the initial phase of an architecture development cycle. It includes information about the following activities -
- Defining the scope
- Identifying the stakeholders
- Creating the architectural vision statement
- Obtaining the initial approval
Business Architecture Evolution
The Business Architecture Evolution phase describes the development of a Business Architecture and its alignment to support an agreed Architecture Vision.
Information Systems Architecture Definition
The Information Systems Architecture Definition phase describes the development of Information Systems Architectures required to support the Architecture Vision. This phase typically involves -
- Identification and development of Data Architectures
- Development of various Application Architectures
Technology Architecture Evolution
The Technology Architecture Evolution phase describes identification and development of the requisite Technology Architecture, with respect to supporting the Information Systems Architecture.
Opportunities & Solutions Identification
The Opportunities & Solutions Identification phase typically involves the following activities -
- Conducting initial implementation planning
- Identifying single or multiple delivery channels for the requisite architectures
Migration Planning
The Migration Planning phase addresses the formulation of a set of detailed sequence of transition architectures with a supporting Implementation and Migration Plan.
Implementation Governance
The Implementation Governance phase involves providing an architectural oversight of the implementation.
Comments